Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Topic Contents
Childhood Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin Treatment (PDQ®): Treatment - Patient Information [NCI]
This information is produced and provided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The information in this topic may have changed since it was written. For the most current information, contact the National Cancer Institute via the Internet web site at http://cancer.gov or call 1-800-4-CANCER.
General Information About Childhood Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin
Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin.
The skin is the body's largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis (upper or outer layer) and the dermis (lower or inner layer). Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
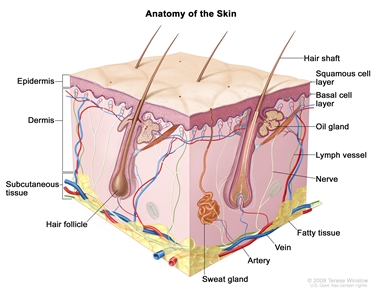
Anatomy of the skin showing the epidermis (including the squamous cell and basal cell layers), dermis, subcutaneous tissue, and other parts of the skin.
Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it usually occurs in skin that is exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands.
Different types of cancer start in the skin.
There are two main forms of skin cancer:
- Nonmelanoma: Skin cancer that forms in basal cells is called basal cell carcinoma. Skin cancer that forms in squamous cells is called squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin are two types of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
- Melanoma: Skin cancer that forms in the melanocytes (cells that color the skin) is called melanoma. In children and adolescents, melanoma is more common than both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. See the PDQ summary on Childhood Melanoma for more information.
Exposure to sunlight affects the risk of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your child's doctor if you think your child may be at risk.
Risk factors for childhood basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight (such as from tanning beds).
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue or green or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
- Having actinic keratosis.
- Having Gorlin syndrome.
- Past treatment with radiation.
- Having a weakened immune system.
Signs of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include a raised lump and a sore that does not heal.
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin or by other conditions.
Check with your child's doctor if your child has any of the following:
- A sore that does not heal.
- Areas of the skin that are:
- Small, raised, smooth, shiny, and waxy.
- Small, raised, and red or reddish-brown.
- Flat, rough, red or brown, and scaly.
- Scaly, bleeding, or crusty.
- Similar to a scar and firm.
Tests that examine the skin are used to diagnose basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
The following tests and procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient's health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Skin exam: A doctor or nurse checks the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture.
- Biopsy: All or part of a growth that doesn't look normal is cut from the skin and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are three main types of skin biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A sterile razor blade is used to "shave off" the growth that does not look normal.
- Punch biopsy: A special instrument called a punch or a trephine is used to remove a circle of tissue from the growth that does not look normal.
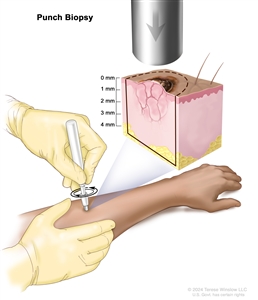
Punch biopsy. A sharp, hollow, circular instrument is used to remove a small, round piece of tissue from a lesion on the skin. The instrument is turned clockwise and counterclockwise to cut about 4 millimeters (mm) down to the layer of fatty tissue below the skin and remove the sample of tissue. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body. - Incisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove part of an abnormal-looking growth.
- Excisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove the entire growth.
Treatment of Childhood Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin
The main treatment for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is surgery. Two types of surgery may be used:
- Excision: The tumor and a small amount of healthy tissue around the tumor is removed.
- Mohs micrographic surgery: The tumor is cut from the skin in thin layers. During surgery, the edges of the tumor and each layer of tumor removed are viewed through a microscope to check for cancer cells. Layers continue to be removed until no more cancer cells are seen. This type of surgery removes as little normal tissue as possible and is often used to remove skin cancer on the face.
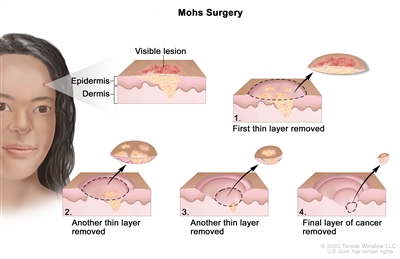
Mohs surgery. A surgical procedure to remove a visible lesion on the skin in several steps. First, a thin layer of cancerous tissue is removed. Then, a second thin layer of tissue is removed and viewed under a microscope to check for cancer cells. More layers of tissue are removed one at a time until the tissue viewed under a microscope shows no remaining cancer. This type of surgery is used to remove as little normal tissue as possible.
To Learn More About Childhood Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin
For more information from the National Cancer Institute about childhood basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, see the following:
- Skin Cancer (Including Melanoma) Home Page
- Skin Cancer Prevention
- Skin Cancer Screening
- Moles to Melanoma: Recognizing the ABCDE Features
For more childhood cancer information and other general cancer resources, visit:
- About Cancer
- Childhood Cancers
- CureSearch for Children's Cancer
- Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer
- Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer
- Children with Cancer: A Guide for Parents
- Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- Cancer Staging
- Coping with Cancer
- Questions to Ask Your Doctor about Cancer
- For Survivors, Caregivers, and Advocates
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government's center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service (CIS), NCI's contact center, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as "NCI's PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary]."
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Childhood Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/skin/patient/child-skin-treatment-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>.
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website's E-mail Us.
Last Revised: 2020-11-02
If you want to know more about cancer and how it is treated, or if you wish to know about clinical trials for your type of cancer, you can call the NCI's Cancer Information Service at 1-800-422-6237, toll free. A trained information specialist can talk with you and answer your questions.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Ignite Healthwise, LLC.



